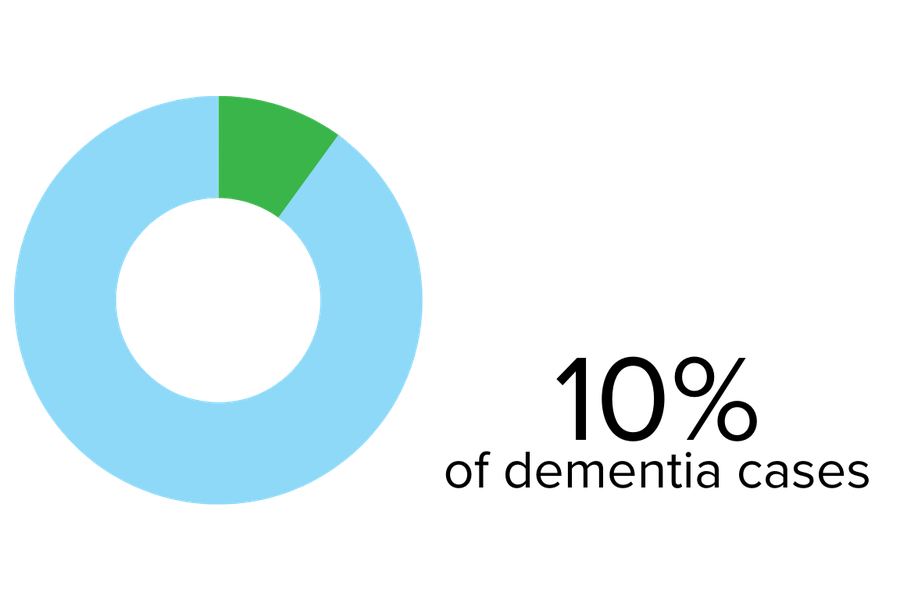Talk to your doctor if you or someone close to you has symptoms of Vascular dementia.
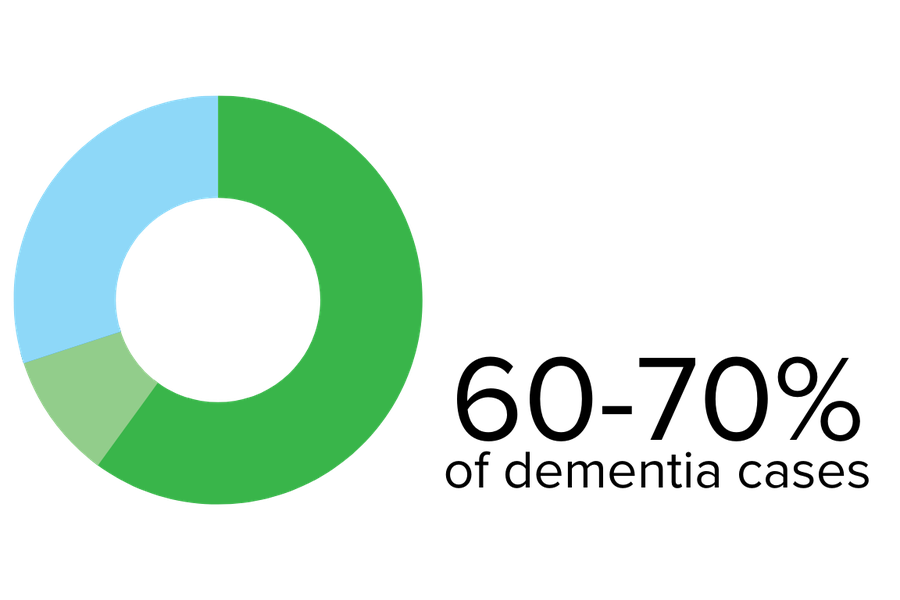
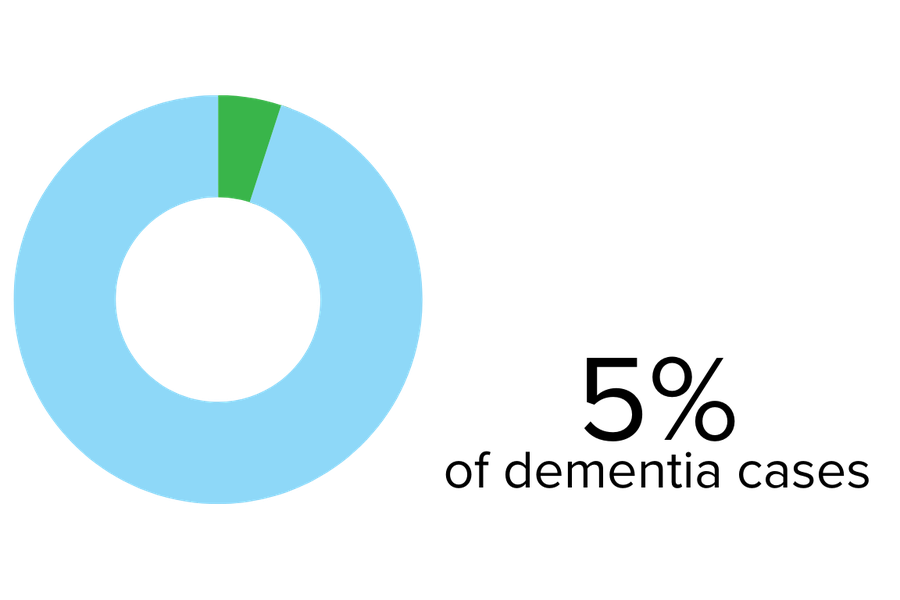
Vascular dementia is the second most common type of dementia in older adults after Alzheimer’s.
Vascular dementia, also called vascular cognitive impairment, is the most preventable type of dementia because it is closely linked to the health of the cardiovascular system (heart and blood vessels). When the blood vessels that supply blood to the brain are damaged, it can lead to the death of brain cells and negatively impact brain function.
Symptoms of vascular dementia can be like those of Alzheimer’s, and both conditions can happen simultaneously (a condition called “mixed dementia”). Symptoms often appear suddenly after a major stroke or leakage of blood in the brain. They may also appear gradually through a series of strokes. The symptoms follow a step-by-step progression.
Risk factors
Risk factors for vascular dementia are the same as those of cardiovascular disease, including smoking, high blood pressure, diabetes, high cholesterol, physical inactivity, and a high-carb high-fat diet.
Reduce your risk
- Keep your blood pressure, blood sugar, cholesterol and body weight in the recommended ranges.
- Follow healthy lifestyle choices: regular exercise, avoid smoking, and limit drinking alcohol.